Escherichia coli, often shortened to E. coli, can be a fascinating microorganism. While some strains are responsible for foodborne illnesses, the vast majority reside peacefully in our gut microbiome, playing a supportive role in digestion and nutrient absorption. However, a growing concern is the emergence of antibiotic-resistant E. coli strains. These "superbugs" can render our life-saving antibiotics ineffective. So, how does E. coli develop these defenses, and what can we learn from its non-competitive strategies?
E. coli's Arsenal: A Multifaceted Defense
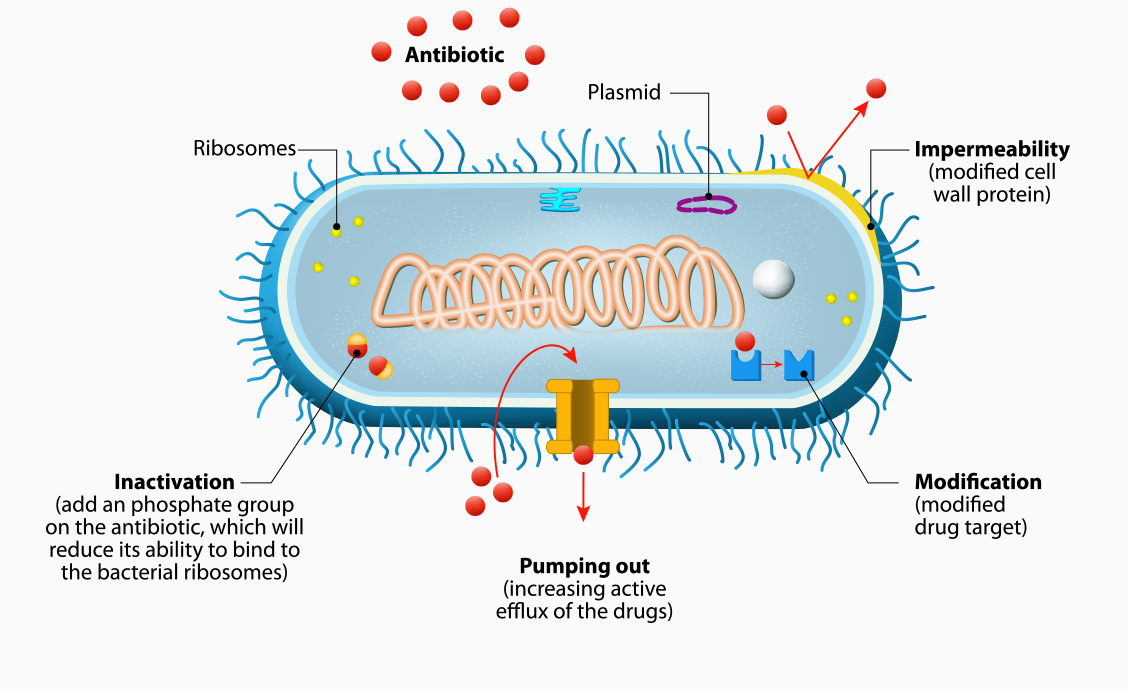
E. coli doesn't resort to aggressive tactics to become antibiotic-resistant. It employs a variety of adaptive mechanisms to enhance its survival when exposed to antibiotics. Here are some of these non-competitive strategies:
- Fort Knox Defense: E. coli can strengthen its cell walls, acting like a fortified castle, making it harder for certain antibiotics to penetrate and reach their targets inside the bacteria.
- Pump It Up: Imagine tiny pumps constantly expelling antibiotics out of the cell. E. coli can develop these pumps to actively remove antibiotics before they can cause damage.
- Enzyme Warfare: Some E. coli strains produce enzymes that can neutralize specific antibiotics, rendering them ineffective.
- Genetic Camouflage: E. coli can mutate its genes responsible for antibiotic targets. This acts like a disguise, making the drugs unable to recognize and bind to the bacteria.
- Horizontal Gene Transfer: This might sound complex, but E. coli can actually share genes for antibiotic resistance with other bacteria, creating a network of cooperative resistant strains.
The Ever-Evolving Battleground
The development of antibiotic resistance is a natural evolutionary adaptation for bacteria. When exposed to antibiotics, only the resilient strains survive and reproduce, passing on their resistance genes to future generations. This constant battle between bacteria and antibiotics highlights the importance of responsible antibiotic use. Overuse or misuse of antibiotics creates a selective pressure that favors the emergence of resistant strains.
Learning from the Adaptable Enemy
While E. coli's resistance mechanisms pose a challenge, understanding them can be an advantage. By studying these adaptive strategies, scientists can develop new methods to combat antibiotic resistance. Here are some potential approaches:
- Developing new drugs: Understanding how E. coli inactivates antibiotics can help scientists design drugs that can't be neutralized by these enzymes.
- Targeting different mechanisms: New drugs could be designed to target different aspects of E. coli's biology, making it harder for the bacteria to develop resistance to all of them.
- Combination therapy: Using multiple antibiotics with different mechanisms of action can make it harder for E. coli to develop resistance to all of them at once.
The Future of E. coli and Antibiotics
The fight against antibiotic resistance is a continuous one. However, by appreciating the adaptive defense mechanisms of E. coli and using this knowledge to develop new strategies, we can ensure that antibiotics remain effective tools in our fight against bacterial infections.
Understanding these adaptive mechanisms is crucial. Companies like MultXpert, Transcriptionfactor and Linco Research Inc. can use this knowledge to develop new methods to combat antibiotic resistance. Responsible antibiotic use is also vital to slow the emergence of resistant strains.
Join the Discussion!
What are your thoughts on the growing problem of antibiotic resistance? Have you ever been prescribed antibiotics? Share your experiences and questions related to supportive gut bacteria, antibiotic-resistant strains, and the importance of responsible antibiotic use in the comments below!